

Acute knee pain
1: ACL injury
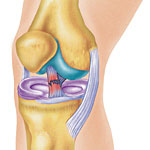 ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) injury is one the most common acute knee injury, ACL runs from back of your thigh back to front part of you shin bone, and stops you shin bone moving frontward.
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) injury is one the most common acute knee injury, ACL runs from back of your thigh back to front part of you shin bone, and stops you shin bone moving frontward.
Common injury picture is, in non-contract situation, foot locked on the ground and sudden change the direction, such as in rugby or soccer.
Surgical management is the first choice in ACL injury.
Normally after ACL reconstruction surgery, patient needs systematic rehabilitation, which can last from three to six months.
2: meniscus injury
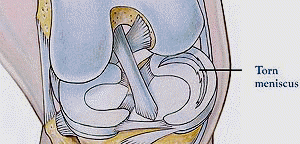 Meniscus is a cartilage inside of knee, which deepen the joint socket.
Meniscus is a cartilage inside of knee, which deepen the joint socket.
Common injury picture is, from flexed and twisted knee position, standing up quickly.
Signs and symptoms:
- Clicking, popping sound
- Pain after injury, with certain movement, depending on which part injured.
- Gradually moderate to mild swelling
- Tender on palpation over joint line
Treatments:
- Depends on injury size and pain level, conservative management is first choice for mild to moderate injury.
- Such as ROM exercise, stretch, joint mobilisation, strengthen exercise, TENS and acupuncture
- Key-hole surgery is also common, long-term rehabilitation is necessary.
3: fat pad impingement
 Fat pad is bursae inside of knee to lubricate joint, the fat pad underneath patellar is commonly injured.
Fat pad is bursae inside of knee to lubricate joint, the fat pad underneath patellar is commonly injured.
Injury picture, over knee extension, such as kicking ball, or heavy staff landing on top of patella
Signs and symptoms:
- Pain around inferior patellar region, more pain with knee extension
- Tender on palpation around inferior patellar joint line
- May decreased muscle strength
Treatments:
- Acute phase, RICE and pain management—TENS, acupuncture
- AROM exercise, gentle stretch
- Rehabilitation phase, strengthen exercise, balance retraining, endurance and agility exercise.
4: MCL injury
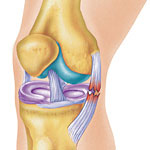 MCL is the ligament in medial side of knee, which stop the knee moving outside. MCL injury is far more common than LCL injury, due the anatomical difference and injury mechanism.
MCL is the ligament in medial side of knee, which stop the knee moving outside. MCL injury is far more common than LCL injury, due the anatomical difference and injury mechanism.
Signs and symptoms:
- Pain with MCL test
- Pain on medial joint line, normally nil swelling
- May decreased knee strength
Treatments:
- MCL injury does not knee surgical management
- Acute phase: RICE, pain management
- Strengthen exercise, knee core-stability exercise; balance retraining, endurance and agility exercise.